ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Home > Products > Prisms > Equilateral Prisms
Fused Silica Equilateral Prism
Fused silica equilateral prism is an equilateral triangular prism made of fused silica with unique optical properties and is widely used in optical systems in the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS) to near-infrared (NIR) wavelengths.
Share this:
The following is a detailed characterization and application analysis:
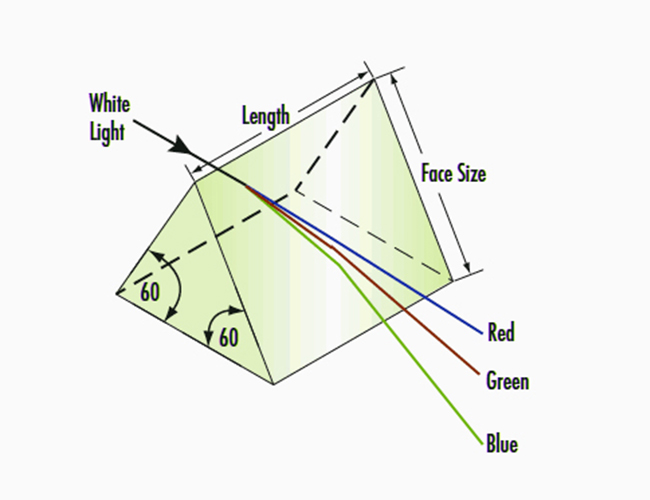
Basic structure of an equilateral prism
Geometry: the cross-section is an equilateral triangle with three sides of equal length and three interior angles of 60°.
Material: common optical glass (e.g. BK7, fused silica) or transparent plastic (e.g. acrylic), different materials affect the refractive index and dispersion properties.
What are the advantages of fused silica equilateral prisms?
Excellent Optical Properties
High transmittance: fused silica or crystal has high transmittance in the UV to NIR (170nm-2500nm) wavelength, especially suitable for UV optical systems.
Low chromatic dispersion: high Abbe number, low chromatic dispersion, reduced chromatic aberration, suitable for applications requiring broad spectrum or precise control of monochromatic light (e.g. laser systems, spectrometers).
Stable Physicochemical Properties
High temperature resistance: can withstand high temperatures (softening point of fused silica is about 1700°C), suitable for high temperature environments (e.g. laser processing, aerospace optics).
Corrosion resistance: resistant to acid, alkali and humid environment, more durable than ordinary optical glass.
Low coefficient of thermal expansion: excellent thermal stability, small deformation during temperature change, suitable for high-precision instruments (such as interferometers, astronomical telescopes).
Basic structure of an equilateral prism
Geometry: the cross-section is an equilateral triangle with three sides of equal length and three interior angles of 60°.
Material: common optical glass (e.g. BK7, fused silica) or transparent plastic (e.g. acrylic), different materials affect the refractive index and dispersion properties.
What are the advantages of fused silica equilateral prisms?
Excellent Optical Properties
High transmittance: fused silica or crystal has high transmittance in the UV to NIR (170nm-2500nm) wavelength, especially suitable for UV optical systems.
Low chromatic dispersion: high Abbe number, low chromatic dispersion, reduced chromatic aberration, suitable for applications requiring broad spectrum or precise control of monochromatic light (e.g. laser systems, spectrometers).
Stable Physicochemical Properties
High temperature resistance: can withstand high temperatures (softening point of fused silica is about 1700°C), suitable for high temperature environments (e.g. laser processing, aerospace optics).
Corrosion resistance: resistant to acid, alkali and humid environment, more durable than ordinary optical glass.
Low coefficient of thermal expansion: excellent thermal stability, small deformation during temperature change, suitable for high-precision instruments (such as interferometers, astronomical telescopes).
| Comparison of fused silica and other material prisms | |||
| Characteristic | Fused Silica Prism | Glass Prism | CaF2 Prism |
| Transmission Range | 180nm – 2.5μm | 350nm – 2μm | 130nm – 8μm |
| UV Transmittance | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Laser Induced Damage Threshold | High | Middling | Middling |
| Cost | Middling | Low | High |

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

